Sluggish Growth in Bonsai: Recognizing and Resolving Underlying Issues
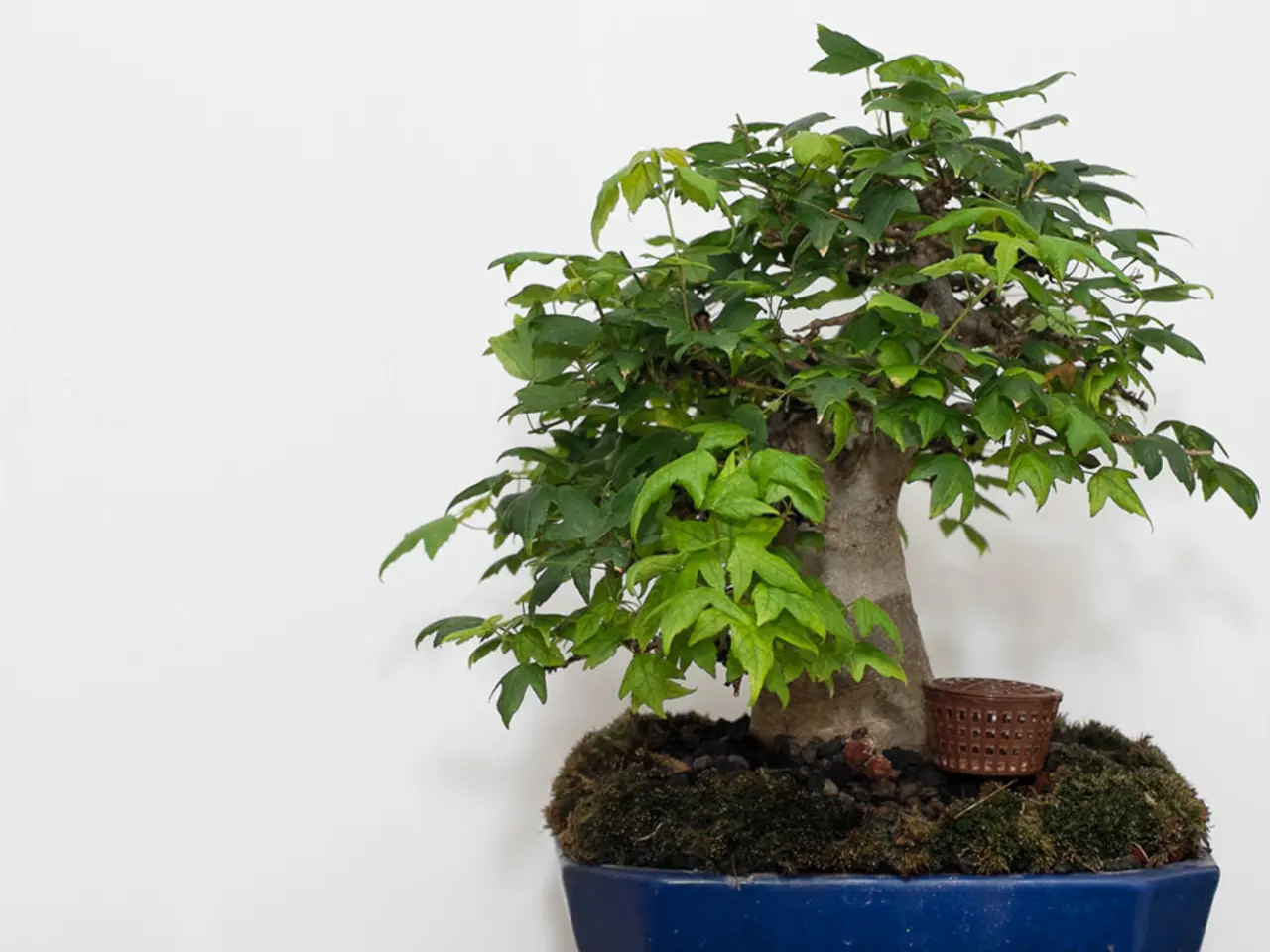
Bonsai trees, miniature living works of art, require careful attention to thrive. Here are some essential tips to help you maintain a healthy and beautiful bonsai.
First and foremost, regular pruning is crucial for the growth of bonsai trees. The frequency depends on the species and growth rate, typically every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. However, it's important to note that some Bonsai species may grow slower due to their genetic predisposition or as they mature with age.
Light exposure is another vital factor for bonsai growth. A north-facing window, heavily shaded outdoor location, insufficient artificial lighting, and seasonal changes can result in inadequate light exposure, leading to weak and spindly trees with pale or yellowish leaves and sparse foliage.
Extreme temperature fluctuations can cause stress to Bonsai trees, leading to slowed growth, defoliation, or even tree death. Most Bonsai species thrive in a temperature range of 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C). Sudden drops in temperature can cause Bonsai trees to shut down growth processes, while prolonged heatwaves can lead to water loss and damage.
Poor air circulation can lead to a buildup of moisture, increased disease susceptibility, and reduced gas exchange, stunting Bonsai growth and beauty. Tight, enclosed spaces, dense canopies, insufficient spacing, and inadequate pruning can result in poor air circulation.
A specialized potting mix, designed for ideal drainage and aeration, is essential for promoting healthy root development and overall Bonsai growth. This mix helps prevent waterlogging and ensures the roots receive adequate oxygen.
Common factors that impede bonsai tree growth include fungal diseases, root rot, pests, inadequate watering, poor airflow, insufficient root space, and environmental stresses such as frost exposure. These can be addressed with proper care practices tailored to the bonsai's unique requirements.
Fungal diseases and root rot are often caused by excessive watering, poor drainage, stagnant or dirty soil, and high humidity conditions that encourage fungal growth. To prevent this, ensure proper watering schedules, good soil drainage, and maintain clean soil with adequate airflow.
Pests can infest bonsai trees, weakening their health. Regular inspection and timely treatment with appropriate pest controls (organic or chemical, depending on severity) help manage pest problems effectively.
Limited root space due to small containers can stress the tree. Managing this requires periodic root pruning and repotting to refresh the soil and allow some root growth. Regular pruning of roots and branches keeps the bonsai healthy and balanced.
Environmental stresses, such as frost sensitivity, are higher in bonsai compared to trees in nature due to their limited root insulation and smaller root mass. Protect bonsai from cold by providing buffers for temperature drops beyond typical hardiness zones, especially after major pruning that weakens the tree.
Mechanical decay and fungal attack on deadwood parts can occur in bonsai with deadwood features. Avoid prolonged exposure of deadwood to moisture and treat deadwood surfaces as necessary to prevent decay.
General care errors, such as over or under-pruning, improper watering, and lack of airflow, are common causes of bonsai decline. Educating oneself on species-specific care and following best practices in pruning can prevent major harm.
Addressing these factors involves maintaining balanced watering to avoid waterlogging or drought stress, ensuring proper soil composition and cleanliness, providing adequate airflow and avoiding excessive humidity, regular inspection for pests and diseases with prompt treatment, periodic root and branch pruning to manage size and health, protecting bonsai from extreme cold, especially after pruning, and managing deadwood carefully to inhibit fungal decay.
It's possible to grow a Bonsai from a seed, but buying a pre-trained tree provides a head start, allowing focus on refining and nurturing the Bonsai. A Bonsai can recover from a period of neglect within several months to a year, depending on the severity of neglect and quality of subsequent care.
Understanding the unique characteristics of a Bonsai species can help tailor care and patience accordingly to appreciate the subtle beauty of their gradual development. Neglect can slow the growth of a Bonsai tree, but with prompt intervention, it can be revived and its growth can be restored.
With these tips in mind, you'll be well on your way to maintaining a healthy and beautiful bonsai. Happy growing!
[1] "Bonsai Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Keeping Your Bonsai Healthy." Bonsai Empire, bonsaiempire.com/blog/bonsai-care-guide/. [2] "Bonsai Diseases and Pests." Bonsai4me, bonsai4me.com/bonsai-diseases-pests/. [3] "Bonsai Pruning: A Guide to Pruning Your Bonsai." Bonsai Empire, bonsaiempire.com/blog/bonsai-pruning-guide/. [4] "Bonsai Root Pruning: A Guide to Pruning Bonsai Roots." Bonsai Empire, bonsaiempire.com/blog/bonsai-root-pruning-guide/. [5] "Winter Care for Bonsai Trees." The Bonsai Garden, thebonsaigarden.com/winter-care-for-bonsai-trees/.